Brillouin Scattering Theory
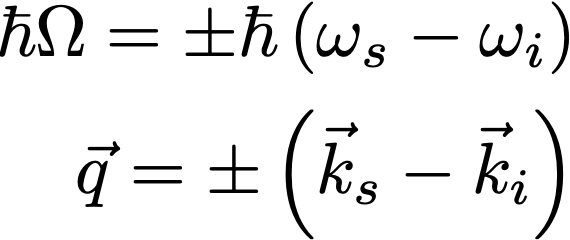
where k is the incident or scattering wavevector and w is the incident or scattering frequency.
This can be graphically represented as is shown below where the wavy line indicates the created or annhilated phonon:
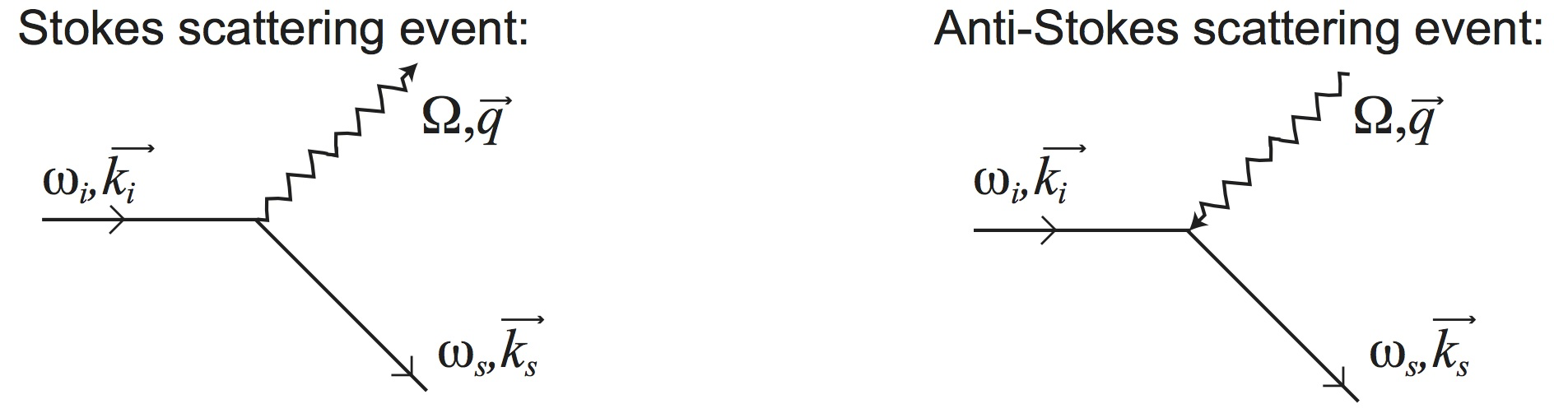
The measured freuency shift of the light is equal to that of the phonon and it's wave vector (q) can be found from the above equations and is given by:
Thus, the Brillouin longitudinal frequency shift as related to the longitudinal sound velocity is given by:
